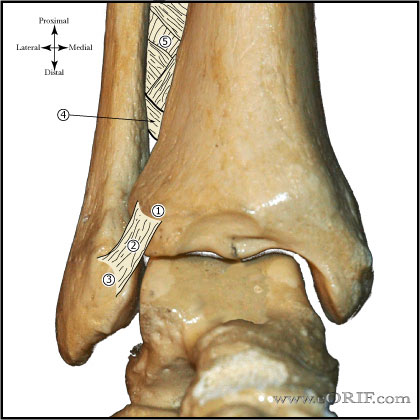
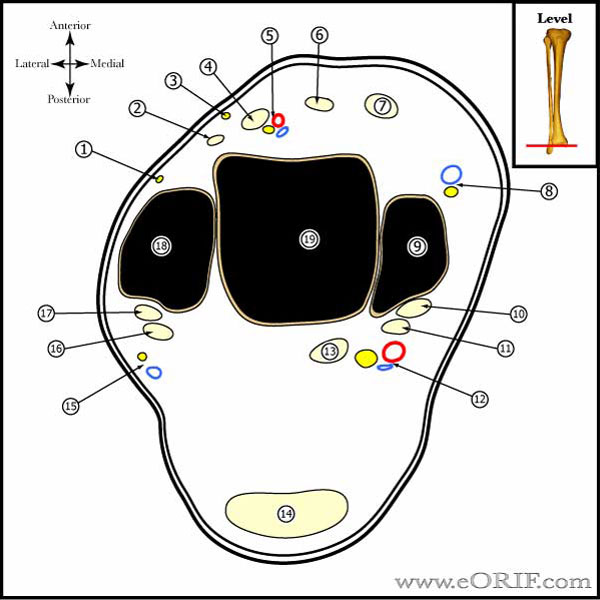
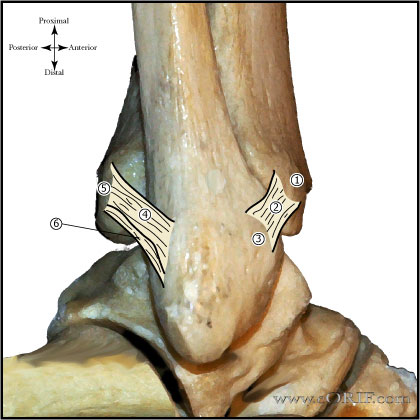
synonyms:Brostom-Gould procudure, lateral ankle ligament reconstruction, ankle instability repair, Brostrom-Gould CPT
Brostrom-Gould Contraindications
Brostrom-Gould Pre-op Planning / Special Considerations
Brostrom-Gould Follow-up
Brostrom-Gould Review References Colville MR, JAAOS 1998;6:368 |