|
|
synonyms: elbow stiffness, elbow contracture, frozen elbow
- <1 yrs duration = stretching exercises, dynamic splinting, and adjustable static night splints
- surgical release for contracture >30 degrees that has failed non-op management. Results of surgical relase for contracture <30 degrees is unpredictable
- Anterior capsulectomy and CPM (Gates HS III, JBJS 74A;1229;1992)
Elbow Contracture ICD-9
- 718.42 (elbow contracture)
Elbow Contracture Etiology / Epidemiology / Natural History
- Loss of terminal extension is typically well tolerated, except in gymnasts and basketball players. Loss of flexion affects Activities of Daily Living and is not well tolerated.
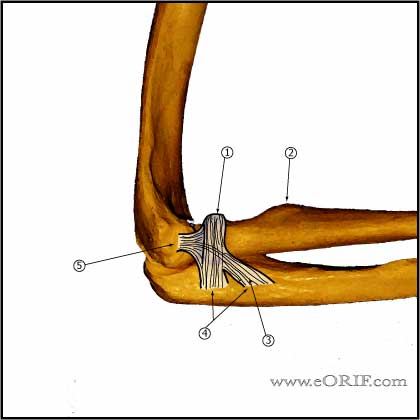
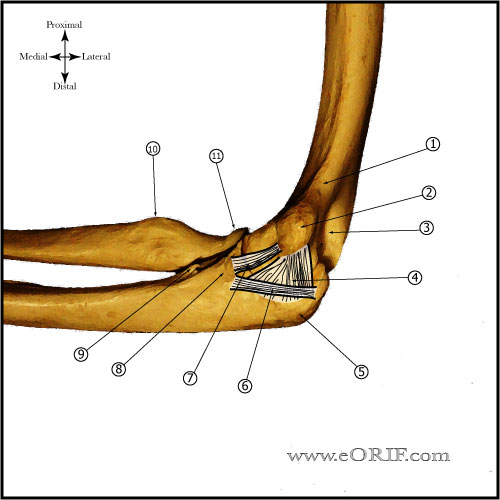
Elbow Contracture Anatomy
- Functional elbow ROM: Flex/extend 30° -130° , pronatation = 50° , supination = 50° (Morrey BF, JBJS 63A;872:1981).
Elbow Contracture Clinical Evaluation
- Complain of pain and limited ROM
- Document ulnar nerve function.
- Note any prior incisions or skin grafts(burns)
Elbow Contracture Xray / Diagnositc Tests
Elbow Contracture Classification / Treatment
- Initial Treatment: physical therapy with static progressive splinting. (Doornberg JN, JOT 2006;20:400).
- Arthroscopic release (Nguyen D, Arthroscopy 2006;22:842) (Ball CM, JSES 2002;11:624),
-See Elbow Arthroscopy
-Anterior capsule is release with a blunt-tipped obturator using a sweeping motion from distal to proximal to increase the joint space.
-Synovial is debrided with shaver, always keep shaver directed toward bone, minimize use of suction.
-Sharp capsular release is then perform using an arthroscopic bitter from lateral to medial.
-Capsule debrided with shaver.
-Gentle manipulation should then allow full extension. Consider viewing form lateral portal to ensure anteromeidal capsule was released. Record post-operative motion.
- Open capsular release 24006 (Marti RK, Acta Orthop Scand 2002;73:144). (Tan V, J Trauma 2006;61:673).
- Consider prophylactic ulnar nerve decompression or transposition in patients with 90°-100° flexion deficits, to decrease risks of post-operative ulnar neuropathy.
Elbow Contracture Associated Injuries / Differential Diagnosis
Elbow Contracture Complications
- Continued stiffness
- Ulnar nerve palsy
Elbow Contracture Follow-up Care
- Post-op: place in extension with an anterior splint to maintain maximum extension for 24-48 hours.
- 2 Days: Splint removed. Evaluate ROM. Start active and active assisted ROM with goals of full flexion/extension, supination/pronation.
- 2 Weeks: Evaluate ROM/Progress.
- 3Weeks: Evaluate ROM. Consider manipulation under anesthesia if motion is not continueing to improve significantly. Consider static progressive splinting.
Elbow Contracture Review References
|



