 |
Nondisplaced
- Garden 1 &2
- Treatment = in-situ parallel screw fixation.
- C-arm, cannulated screw set, supine on fx table. Place guide pin in center-center location. 3 screws total, insignificant mechanical advantage to adding more implants.
- See also AO Classification.
|
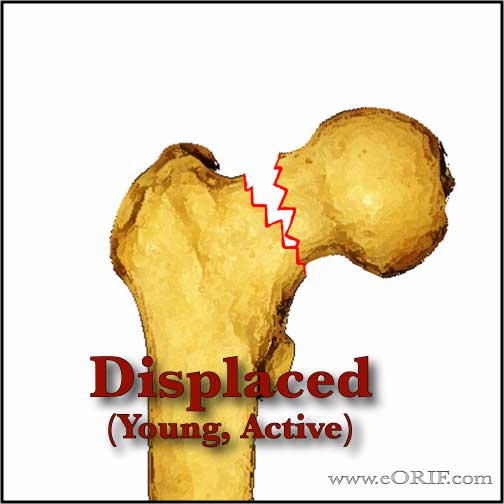 |
Displaced, Young active patient
- Garden III & IV
- Treatment = closed reduction and internal fixation.
- Fixation is generally performed with 3 parallel screws.
- Open reduction is indicated if closed reduction is unsatisfactory.
- Young patients with isolated, high energy femoral neck fracture are at high risk for nonunion & AVN. (Swiontkowski MF, JBJS 1984;66A:837).
- Consider dynamic hip screw with derotational screw for vertical or severely comminuted fractures.
- 25% nonunion risk(Rx-valgus osteotomy)
- 30% osteonecrosis risk(Rx=arthroplasty).
- See also AO Classification.
|
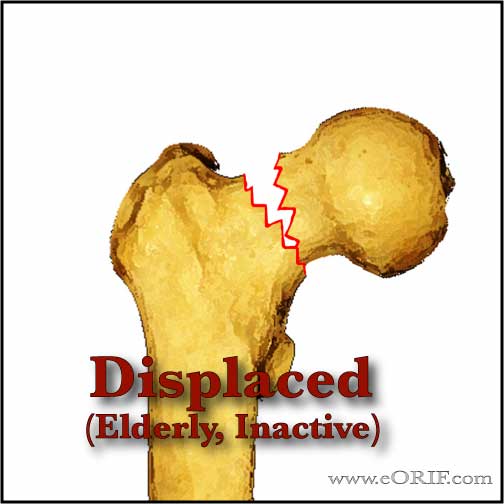 |
Displaced, Elderly inactive patient
- Garden III & IV
- Treatment = primary prosthetic replacement.
- Hemiarthroplasty for patients without underlying arthritis or risk of dislocation (Parkinson's, prior stroke, neuro impairment).
- THAfor patients with underlying arthritis.
- Hemiarthroplasty generally performed with a cemented modular unipolar prosthesis. The clinical benefits of bipolar designs are questionable and are generally not consider to warrant the added expense.
- Surgery should be performed ASAP after medical clearance, usually within 24-48 hours. Medical conditions should be stabilized before surgery. (Sexson SB, JOT 1988;1:298)
- Anestesia: type has not been shown to affect outcomes. (Davis FM, Br J Anaesth 1987;59:1080)
- See also AO Classification.
|





