 |
synonyms:tumb MP dislocation, thumb metacarpophalangeal (MP) joint dislocation, thumb MCP dislocation
Tumb MCP Dislocation ICD-10
A- initial encounter
D- subsequent encounter
S- sequela
Tumb MCP Dislocation ICD-9
- 834.01 Closed dislocation, metacarpophalangeal joint
- 834.11 Open dislocation, metacarpophalangeal joint
Tumb MCP Dislocation Etiology / Epidemiology / Natural History
Tumb MCP Dislocation Anatomy
- Thumb MCP joint is stabilized by proper collateral ligaments, accessory collateral ligaments, the joint capsule, intrinsic musculature, and extrinsic tendons.
- Sesamoids are embedded in the volar plate and lie anterior to and articulate with the metacarpal head
- Flexor pollicis brevis and abductor pollicis brevis muscles partially insert into the sesamoids
Tumb MCP Dislocation Clinical Evaluation
- Pain and swelling in the thumb
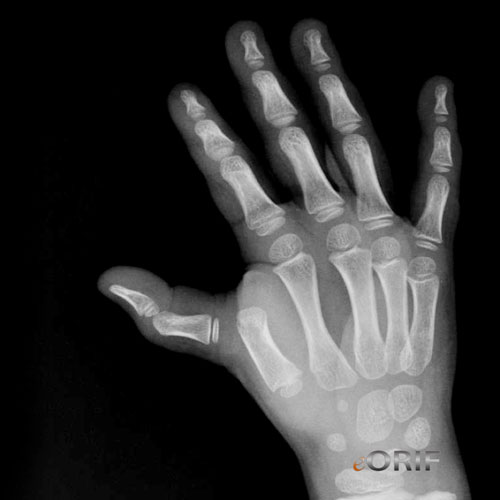
Tumb MCP Dislocation Xray / Diagnositc Tests
- A/P, lateral and oblique views of the thumb indicated.
Tumb MCP Dislocation Classification / Treatment
- Simple dislocation of the mcp joint of the thumb will show proximal phalanyx to be nearly perpendicular to the metacarpal. Reducible closed. Rx:thumb spica cast. Failed closed reduction indicates volar plate is interposed in the joint or metacarpal head is buttonholed through the palmar structures: requires open reduction. Consider ulnar collateral ligament repair if unstable after CR
- Dorsal thumb MCP dislocation: Closed reduction for dorsal dislocation: flex the wrist and the PIP joint to relax the flexor tendons. Apply pressure from dorsal to volar to the base of the proximal phalanx.
- Volar thumb MCP joint dislocation: uncommon. often requires open reduction due to interposed tissue(EPL, EPB, dorsal capsule, volar plate). Closed reduction is generally unsuccessful if there is no palpable EPL, displacement of the EPL or EPB, interposed sesamoids on radiographs, and paradoxical MP joint flexion and interphalangeal joint extension on attempting MP extension. Closed reduction for volar dislocation: Wrist and MCP joint is flexed, and gentle pressure applied to the volar surface of the proximal phalanx as it is brought into extension.
- Complex dislocation prox phalanyx and metacarpal are parallel, volar plate is interposed, irreducible closed
Tumb MCP Dislocation Associated Injuries / Differential Diagnosis
Tumb MCP Dislocation Complications
- Early degenerative arthritis
- Osteonecrosis of the metacarpal head
- Stiffness
- Neurovascular injury
Tumb MCP Dislocation Follow-up Care
- Early ROM with a dorsal blocking splint preventing extension beyond neutral.
Tumb MCP Dislocation Review References
- Bohart PC, JBJS 56A:1459;1974
- Dinh P, JAAOS 2009:17;318-324
- Beck JD, Klena JC. Closed reduction and treatment of 2 volar thumb metacarpophalangeal dislocations: report of 2 cases. J Hand Surg Am. 2011 Apr;36(4):665-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jhsa.2010.12.006. Epub 2011 Feb 25. PubMed PMID: 21353397
- Hirata H, Takegami K, Nagakura T, Tsujii M, Uchida A. Irreducible volar subluxation of the metacarpophalangeal joint of the thumb. J Hand Surg Am. 2004 Sep;29(5):921-4. PubMed PMID: 15465245
|

