|
|
synonyms:
Trapezium Fx ICD-10
A- initial encounter for closed fracture
B- initial encounter for open fracture
D- subsequent encounter for fracture with routine healing
G- subsequent encounter for fracture with delayed healing
K- subsequent encounter for fracture with nonunion
P- subsequent encounter for fracture with malunion
S- sequela
Trapezium Fx ICD-9
- 814.05 (closed fracture of trapzium , larger multangular)
- 814.06 (closed fracture of trapezium, smaller multangular)
- 814.15 (open fracture of trapezium, larger multangular)
- 814.16 (open fracture of trapezium, smaller multangular)
Trapezium Fx Etiology / Epidemiolgy / Natural History
- uncommon: generally from high energy trauma, MVA
- Natural History: displaced fractures can lead to permanent limitations in pinch and grip strength as well as post-traumatic arthritis
Trapezium Fx Anatomy
Trapezium Fx Clincal Evaluation
- tenderness and swelling localized to trapeziometacarpal joint / base of thumb
- Motion may be pain free in trapezial ridge fractures, but pinch strength will be weakened and/or painful
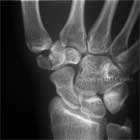
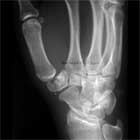
Trapezium Fx Xray
- Standard P/A, lateral and oblique views of the wrist
- Bett's view: beam is directed toward trapeziometacarpal/scaphotrapezial joints with wrist pronated and hypothenar emminence resting on the cassette.
- Carpal Tunnel view
- Consider getting comparison views of normal wrist, or CT scan if diagnosis is not definitive on plan films.
Trapezium Fx Classification/Treatment
- Vertical split: Generally found to be comminuted at surgery
- Trapezial Ridge Fx: Type I occur at the base of the ridge = thumb spica. Type II=tip of ridge=symptomatic treatment, can be excised if remains symptomatic(Palmer AK, J Hand Surg 1981;6:561-564)
- Non-displaced fx = thumb spica cast for 4-6weeks
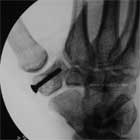
- Displaced = articular displacement >2mm or carpometacarpal subluxation = ORIF with or without bone grafting. Fixation with k-wires, mini-fragment screws, Herbert screws, etc.
Trapezium Fx Technique
- Antibiotic, tourniquet
- 4-5cm longitudinal incision over radial wrist centered on trapezium
- Identify and retract sensory branch of radial nerve ulnarly
- Retract EPL and radial artery ulnarly
- Retract APL and EPB palmarly
- Incise capsule and expose trapezium
- Irrigate hematoma, reduce fx generally with 0.045-in K-wire
- Fixation with K-wires, mini-fragment screws (2.0mm), Acutrak screw, or Herbert screws
- Irrigate
- Close in layers
- Thumb spica splint
Trapzium Fracture Associated Injury / Differential Diagnosis
- Bennett's Fx
- Distal radius Fx
- Scaphoid Fx
Trapzium Fx Complications
- continued pain, weakness in pinch and progessive degenerative changes may occur even after union. Consider LRTI for refractory cases.
- Radial artery, sensory branch of radial nerve injury
- malunion, nonunion
- post-traumatic arthritis
Trapzium Fx Follow-Up
- Post-Op: Place in volar splint. Encourage digital ROM, elevation.
- 7-10 Days: remove splint. Place in short arm thumb spica cast. Consider removable splint with gentle ROM if fixation was extremely secure.
- 6 Weeks: Cast removed. Check xrays. Started gentle ROM exercises. Activity modifications: no heavy manual labor, no contact sports, no lifting >5 lbs.
- 3 Months: Check xrays. If union is complete return to full activities.
Trapzium Fx References
- McGuigan FX, Culp RW, Surgical Treatment of Intra-articular Fractures of the Trapezium, J Hand Surg 2002;27A;697
|



